On the destination mac (an iMac), setting the 'Configure IPv4' to manually, setting the IP address to what I want, and then setting subnet mask to 255.255.0.0 (this is the subnet mask my MacBook shows) I did this after deleting and recreating Thunderbolt Bridge interface on both iMac and MacBook. To find the MAC address of the device connected to your router—assuming you can access the router's administrative control panel—log in and check for connected devices. Each active device, as well as recently connected devices, should list the local IP address as well as the MAC address.
- How To Find Static Ip Address Mac
- How To Find Manual Ip Mac Address
- How To Find Manual Ip Machine
- How To Find Manual Ip Mac Scanner
- How To Find Manual Ip Mac Os
- MAC is acronym for Media Access Control address. It is a unique identifier attached to almost most all networking equipment such as Routers, Ethernet cards, Switches/Hubs and other devices. If you do not have access to router admin interface (via telnet or webbased gui), use the following method to find out router MAC address.
- Click and select IP Camera, DVR, NVR. If your camera model doesn’t show in the list, you could choose JPT3815. For LAN view, please fulfill them below. For windows, this address is LAN access URL which you can find on page 7 You can find the label on the cameras For Internet view, please fulfill them below. Page 16: For Others.
- Wired MAC Address: Turn the printer ON; Wait for the printer to show ‘Ready’ Press and release 'PAUSE' + 'FEED' + 'CANCEL' (all 3 at the same time). A label should be printed with the 'Network Report' and it will show the MAC Address. If the Network Report cannot be printed, then a Configuration Label needs to be printed.
There may be several reasons why you would like to know the MAC address of a Suprema device:
You do not have a DHCP server and need to give IP address based on a MAC address
You do not know the IP of your device and are having difficulty searching it through BioStar’s search function
You are using static IP but are unsure if you have already allocated the IP address to another device.
Methods to Check the MAC Address
Note: The PC you are using has to be on the same network of the device to use these commands
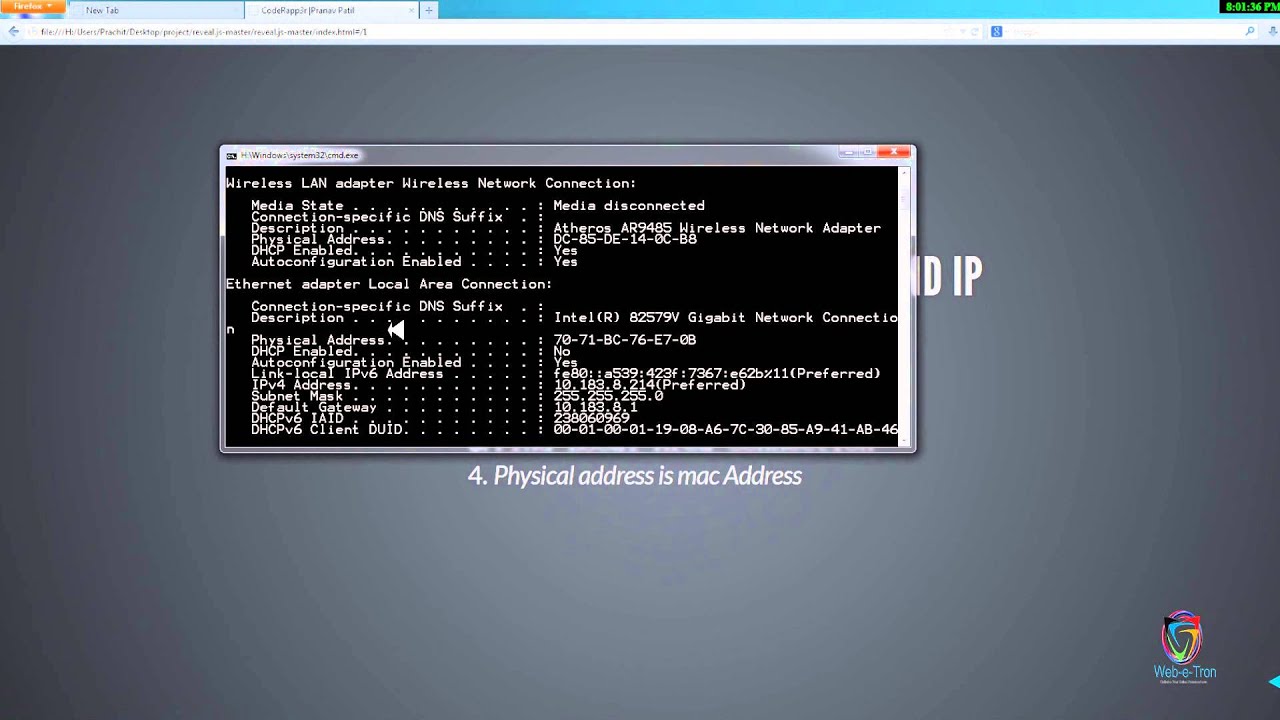
1. Finding IP and MAC addresses of all devices on the local network:
Type ‘arp –a’ on a command prompt
2. Finding a device’s MAC address based on IP address:
Type ‘arp –a [ip address] on a command prompt
Checking Device IP Address Based on the Device ID
If you would like to find the device’s IP based on the MAC address you can follow the steps below.
1.Check your device ID written on the device label on the back of the device.
2.Change the device ID into hexadecimal numbers. One option is to use Windows’ Calculator.
3.Open Windows Calculator and press alt + 3 to change to the programmer’s calculator.
4.Select Dec and input the device ID.
5.Click Hex. Result is 20471BC5. This is going to be the latter half of the MAC address.
6.Check the MAC address chart below to see what the first half of the MAC address will be.
7.My device is an A2, so the MAC address will start with 00-17-FC-47-XX-XX.
8.Hence my MAC should be 00-17-FC-47-1B-C5.
9.Open a command prompt and type arp –a.
10.Search for the device’s MAC address on the list.
11.My device IP is 192.168.16.104.
Suprema Device MAC Address Chart
Suprema devices have the same fixed hexadecimal digit for the first six digits.
The two digits after 00-17-FC are different based on the device model. Please refer to the chart below.
How to Find a Device's IP Address with Wireshark
You can use this option if
Your device does not have a LCD and it’s IP has been configured to a different subnet and you cannot figure it out with arp –a command on command prompt.
Your device has a LCD but you don’t know the admin account and cannot access the menu. Additionally the device has a unknown subnet configured and you can’t search it with arp –a on command prompt.
You can use Wireshark to figure out the IP address of a device with a different subnet.
Note:
- Arp –a command can only search devices within the same subnet.
- If you have 2 network cards, turn one off (i.e Wifi network card) to make sure you are searching from the right network card.
Option 1)
You can download Wireshark from the following link
Follow the procedure below.
1.Install Wireshark.
2.Find the MAC address of the device with the device ID by using the chart above and a calculator.
3.Connect your device with your PC directly with an Ethernet cable.
4.I have a BioStation 2-OMPW and the ID is 546832586.
5.According to the chart above the MAC should start with 00-17-FC-98.
6.When I change ID from dec to hex on the calculator the result is 209800CA.
7.My device’s MAC address is 00-17-FC-98-00-CA.
8.Run Wireshark.
9.Go to Capture > Options…
10.Select your network card interface and click start.
11.Put a filter with the MAC address with the format shown below.
12.Click on the arrow to start the filter.
13.Power off and power on the device. 14.Now you will only see packets that are coming from your device. Wait for 5 minutes if it doesn't appear.
15.Look for the arp request.
16.The device’s ARP request is ‘Who has 10.111.111.1? Tell 10.111.111.111
The 10.111.111.1 is the gateway set on the device
10.111.111.111 is the device IP
17. Connect your device directly to a test PC with BioStar 1 / 2 Server installed using a ethernet cable.
Note: 1.x firmware entry devices cannot be searched in BioStar 2.
1) icon designed by Maxim Basinski from Flaticon
18. Set the test PC IP into the same subnet range of your device.
19. Search and add the device in BioStar and change the device IP.
Option 2)
How To Find Static Ip Address Mac
1) Run Wireshark
2) Select the network which as the devices connected to:
3) Under Capture, enter host 192.168.1.55 (192.168.1.55 is the device IP)
Applies to RouterOS:2.9, v3, v4 +
- 2Properties
Summary
Sub-menu:/ip address
Standards:IPv4 RFC 791
How To Find Manual Ip Mac Address
IP addresses serve for a general host identification purposes in IP networks. Typical (IPv4) address consists of four octets. For proper addressing the router also needs the network mask value, id est which bits of the complete IP address refer to the address of the host, and which - to the address of the network. The network address value is calculated by binary AND operation from network mask and IP address values. It's also possible to specify IP address followed by slash '/' and the amount of bits that form the network address.
In most cases, it is enough to specify the address, the netmask, and the interface arguments. The network prefix and the broadcast address are calculated automatically.
It is possible to add multiple IP addresses to an interface or to leave the interface without any addresses assigned to it. In case of bridging or PPPoE connection, the physical interface may bot have any address assigned, yet be perfectly usable. Putting an IP address to a physical interface included in a bridge would mean actually putting it on the bridge interface itself. You can use /ip address print detail to see to which interface the address belongs to.
MikroTik RouterOS has following types of addresses:
- Static - manually assigned to the interface by a user
- Dynamic - automatically assigned to the interface by DHCP or an estabilished PPP connections
Properties
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| address (IP/Mask; Default: ) | IP address |
| broadcast (IP; Default: 255.255.255.255) | roadcasting IP address, calculated by default from an IP address and a network mask. Starting from v5RC6 this parameter is removed |
| interface (name; Default: ) | Interface name the IP address is assigned to |
| netmask (IP; Default: 0.0.0.0) | Delimits network address part of the IP address from the host part |
| network (IP; Default: 0.0.0.0) | IP address for the network. For point-to-point links it should be the address of the remote end. Starting from v5RC6 this parameter is configurable only for addresses with /32 netmask (point to point links) |
How To Find Manual Ip Machine
Read only properties
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| actual-interface (name) | Name of the actual interface the logical one is bound to. For example, if the physical interface you assigned the address to, is included in a bridge, the actual interface will show that bridge |
How To Find Manual Ip Mac Scanner
Two IP addresses from the same network assigned to routers different interfaces are not valid unless VRF is used. For example, the combination of IP address 10.0.0.1/24 on the ether1 interface and IP address 10.0.0.132/24 on the ether2 interface is invalid, because both addresses belong to the same network 10.0.0.0/24. Use addresses from different networks on different interfaces, or enable proxy-arp on ether1 or ether2.
Example
[Top | Back to Content]
How To Find Manual Ip Mac Os
